Autores
Molina Giraldo, D.A. (UNIVERSIDAD DE CALDAS) ; Rios Vásquez, L.A. (UNIVERSIDAD DE CALDAS) ; Macias L., M.A. (UNIVERSIDAD DE LOS ANDES) ; Ocampo-cardona, R. (UNIVERSIDAD DE CALDAS)
Resumo
Quaternary Ammonium Salts QAS of general structure [Ar2C=CH(CH2)nN(CH3)2CH2X]+ A-
have become attractive targets as potential therapeutic agents. In addition to a
recent comparative crystallographic study which was published on iodide QAS, a
new piece of study was performed involving the analog BF4- exchanged salts, where
Ar= C6H5, p-F-C6H4, or m-F-C6H4; n=2 or 3; and X= H, Cl or I. Very significant
differences were observed in terms of the existence of I‧‧‧I, I‧‧‧F halogen
bonds, C-H‧‧‧π and cation‧‧‧π interactions, proving how the nature of the anion
also determines their supramolecular assembly. These QAS have become interesting
substrates, not only for medical purposes, but also because several interesting
interactions are present in their crystalline structure.
Palavras chaves
Quaternary Ammonium Salts; Halogen-halogen bonding; Supramolecular assembly
Introdução
Ionic liquids, including Quaternary ammonium salts (QAS), are important
substances from an industrial and medicinal point of view, and as such they have
been extensively reviewed (EGOROVA et al., P. 7132, 2017). In particular, QAS
with general structure [Ar2C=CH(CH2)nN(CH3)2CH2X]+ A-, have been subject of
continuous studies aiming to understand and promote their potential use as
therapeutic agents with very promising results as antiprotozoal agents (DUQUE-
BENÍTEZ et al., p. 1, 2016; LÓPEZ-MUÑOZ et al. p. 300, 2019). While research on
the behavior of representative salts against tumoral colo-rectal lines is in due
course, a key piece of this study involves the research of their crystalline
structure and supramolecular interactions. Recent comparative crystallographic
studies were published on iodide salts, with Ar= phenyl groups containing (or
not) fluorine atoms in the para- or meta- position, n=2 or 3 methylene groups,
and X= H, Cl or I (MÚNERA-OROZCO et al., p. 1230, 2015; MOLINA-GIRALDO et al.,
p. 133962, 2023), with a complete description on the existence of I‧‧‧I, CH‧‧‧π
and cation‧‧‧π interactions. These ammonium cations have become interesting
substrates, not only due to their biological attributes, but also because the
halogen-mediated interactions present in their crystalline structure. In this
work, a new piece of study was performed involving BF4- exchanged QAS salts,
becoming even more attractive from a physical point of view with a variety of
supramolecular interactions. Very significant differences were observed, proving
how the nature of the anion also determines their supramolecular assembly. In
particular, I‧‧‧I, I‧‧‧F, CH‧‧‧F, CH‧‧‧I and CF‧‧‧π halogen-mediated
interactions, and (CH/cation‧‧‧π) contacts are described.
Material e métodos
Target QAS were initially prepared and purified as ioidide salts through a known
four-step synthetic pathway (López-Muñoz et al., 2019) and fully characterized
by MS, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR and DEPT. Then, I- anion was changed using AgBF4, giving
rise to QAS of the form [Ar2C=CH(CH2)nN(CH3)2CH2X]+ BF4-, where Ar= C6H5, p-F-
C6H4, or m-F-C6H4; n=2 or 3; and X= H, Cl or I. Crystallization through slow
evaporation method from appropriate solvents rendered pure salts with the proper
crystal sizes for crystallographic study. A diffractometer Agilent SuperNova
Dual Atlas, with radiation CuK (=1,54184Å) was used. The integration of
collected frames and data correction for the absorption effect were performed
with the CrysAlis PRO software package. Structures were resolved using the
iterative method using charge flipping algorithm and refined by least squares F2
using SHELXL 2018/3. Graphical material was elaborated by Mercury 4.1, while
structural calculations were performed using Platon 101019. Intermolecular
interactions were studied by analyzing Hirshfeld surfaces with software
CrystalExplorer 17.5.
Resultado e discussão
Non-covalent halogen-mediated interactions have been documented recently, with
larger halogen atoms behaving as Lewis acid as a consequence of the so-called
sigma hole (MÉNDEZ et al., p. 22, 2017). These and other non-covalent
interactions were observed and the distances were measured in QAS of structure
[Ar2C=CH(CH2)nN(CH3)2CH2X]+ BF4-. As typical examples, compound series 3a and 3b
(where Ar= C6H5, n=2 or 3 respectively and X=I as shown in Fig. 1) were prepared
from the respective iodide salts 2a or 2b by anion exchange with AgBF4.
Figure 1
Also, analysis of Hirshfeld surfaces for compound 3b (Fig. 2) evidences that
only red areas are found in the region of the methyl groups and iodomethyl group
attached to the quaternary nitrogen, with contacts shorter than the Van der
Waals radii in the phenyl groups region. In this salt, C-H‧‧‧F and C-H‧‧‧π are
the only hydrogen interactions. Geometry of these (and other) interactions are
summarized in table 1.
Figure 2
Table 1. Geometry of interactions (Å) in compound 3b
D-H•••A D-H (Å) H•••A (Å) D•••A (Å) D-H•••A (°) Symmetry code
C2A-H2AA•••F1B 0,97 2,46 3,290(6) 144 Asymmetric unit
C18A-H18A•••F1A 0,97 2,32 3,221(10) 155 2-x,1-y,-z
C18B-H18C•••F1B 0,97 2,54 3,416(8) 150 Asymmetric unit
C19A-H19C•••F4A 0,96 2,42 3,321(8) 156 x,1+y,z
C9B-H19D•••F1A 0,97 2,38 3,319(14) 166 1+x,y,z
C20A-H20B•••F2A 0,96 2,41 3,365(10) 172 x,1+y,z
C14A-H14A•••Cg4 0,97 2,97 3,747(7) 142 1+x,y,z
C11B-H11B•••Cg1 0,97 2,80 3,654(5) 153 -1+x,y,z
C-I•••BF4- C-I (Å) I•••BF4- (Å) C•••BF4-(Å) C-I•••BF4- (°) Symmetry code
C17-I1A•••F3 2,127 3,139 5,248 170 Asymmetric unit
It is very noteworthy the C-I...F interaction (distance 2,127 Aº, angle 170º).
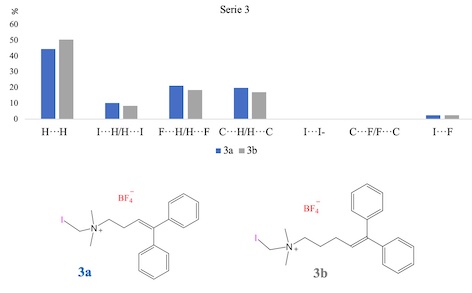
Interactions in crystalline QAS 3a and 3b

Hirshfeld surfaces in QAS 3b
Conclusões
Crystalline [Ar2C=CH(CH2)nN(CH3)2CH2X]+ BF4- salts exhibit mainly C-I‧‧‧F and C-
H‧‧‧F non-covalent interactions (fluorine as acceptor), which are modified
depending of the nature of the anion. C-H‧‧‧I interactions characteristic of
iodide salts are replaced for shorter C-H‧‧‧F distances in tetrafluoroborate
salts, with other distances such as C-H‧‧‧π or C-F‧‧‧π not being substantially
modified. However, two- dimensional fingerprint analyses demonstrate that these
interactions occur at different percentages, so that every minimum structural QAS
modification significantly affects their supramole
Agradecimentos
Authors acknowledge and thank Universidad de Caldas in Colombia (Vicerrectoría de
Investigaciones y Postgrados, project code 0430817) and Universidad de los Andes
in Colombia, for the financial support.
Referências
DUQUE-BENÍTEZ, S. M. et al. Synthesis of Novel Quaternary Ammonium Salts and Their in Vitro Antileishmanial Activity and U-937 Cell Cytotoxicity. Molecules 21, 1–16, 2016
EGOROVA, K. S., GORDEEV, E. G., ANANIKOV, V. P. Biological Activity of Ionic Liquids and Their Application in Pharmaceutics and Medicine. Chem. Rev. 117, 7132–7189, 2017
LÓPEZ-MUÑOZ, M., GÓMEZ-PEÑA, J. J., RÍOS-VÁSQUEZ, L. A. et al. Novel fluorinated quaternary ammonium salts and their in vitro activity as trypanocidal agents. Med. Chem. Res. 28, 300–319, 2019
MENDEZ, L., HENRIQUEZ, G., SIRIMULLA, S. & NARAYAN, M. Looking back, looking forward at halogen bonding in drug discovery. Molecules 22, 22–25, 2017
MOLINA-GIRALDO, D. A., RÍOS-VÁSQUEZ, L. A., TOSCANO, R. A., OCAMPO-CARDONA, R., GÓMEZ-PEÑA, J. J., MACÍAS A., M. M. J. Mol. Structure 1271, 133962, 2023
MÚNERA-OROZCO, C., OCAMPO-CARDONA, R., CEDEÑO, D. L., TOSCANO, R. A. & RÍOS-VÁSQUEZ, L. A. Crystal structures of three new N-halomethylated quaternary ammonium salts. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. E Crystallogr. Commun. 71, Nº. 10, 1230-1235, 2015
















