Autores
Lança, N.C. (IFTO CAMPUS PALMAS) ; Neto, O.C. (IFTO CAMPUS PALMAS) ; Rodrigues, F.M. (IFTO CAMPUS PARAÍSO DO TOCANTINS) ; Viroli, S.L.M. (IFTO CAMPUS PARAÍSO DO TOCANTINS)
Resumo
The hamburger is a widely consumed food, high in fat and calories. The objective
of the study was the elaboration of beef hamburger added with corn flour as a
way to add nutritional value to the product. The physical-chemical analyzes took
place at the IFTO Food Laboratory and followed the methodology of the Adolfo
Lutz Institute. Treatments were carried out with different concentrations of 0%,
5% and 10% of corn cob flour incorporated in the preparation of hamburgers. The
10% corn cob flour formulation presented an average of carbohydrates above the
recommended in the referred legislation. The addition of corn cob flour in the
proportions of 5% and 10% significantly interfered with the values of
carbohydrates, lipids and proteins.
Palavras chaves
Agro-industrial Waste; proximal analysis; Fiber
Introdução
The hamburger is a widely consumed industrialized meat food that has a high
content of saturated fat and caloric value (FERREIRA, 2019). Excessive
consumption of these fats causes an increase in cholesterol and triglyceride
levels, causing cardiovascular diseases, obesity, diabetes, cancers and other
chronic diseases (HAUTRIVE et al., 2008; ORTIGOZA, 2008). The use of vegetable
fibers such as oats, linseed, cassava, peas, sesame, wheat, starch, etc. are
alternatives that are being researched to reduce the saturated fat content of
animal origin in hamburgers (ROCHA, 2015). The use of fiber in the nutritional
increase of the hamburger can collaborate to reduce the saturated fat content
and caloric value, preserve the texture, improve the emulsion and water
retention, benefiting yield and producing a reduction in the costs for the
preparation of meat products. (FERREIRA, 2014). As one of the alternatives for
obtaining the fibers appears the corn cob. Currently, corn on the cob is defined
as waste being used mainly for animal feed on a small scale, providing the
underutilization of this part of the food. The development of corn cob flour
makes it possible to use a raw material rich in fibers, with a high content of
minerals, and allows its use in meat products (FERREIRA, 2014). The inclusion of
corn cob flour in hamburgers is a valid option, however, these flours must offer
the consumer a product of good nutritional and sensory quality (FASOLIN et al.,
2007). In this way, the present study aimed at the elaboration of beef hamburger
added to corn cob flour as a way to add nutritional value to the product.
Material e métodos
Raw materials: beef (85%), textured soy protein (4%), water (9%), sodium
chloride (0.9%), white pepper (0.1%), garlic powder (0.1%), dehydrated onion
(0.1%), dehydrated parsley (0.3%), sodium glutamate (0.4%) and sodium
erythorbate (0.1%) which were acquired by purchasing, in the local commerce of
the City of Paraíso do Tocantins - TO. After acquisition, the raw materials were
transported in their original packaging to the Industrial Kitchen of the Federal
Institute of Education, Science and Technology of Tocantins IFTO - Paraíso do
Tocantins campus, where 3 (three) treatments were performed with different
concentrations of 0%, 5% and 10% corn cob flour incorporated in the preparation
of hamburgers with varying meat content, keeping the other ingredients constant.
For the development of beef hamburger formulations, the Technical Regulation on
Hamburger Identity and Quality (BRASIL, 2000) and the procedures, with
modifications, recommended by Terra (2005) were followed. The physicochemical
analyzes of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins were carried out in triplicate at
the IFTO Food laboratory and followed the methodological procedures of the
Physicochemical Methods for Food Analysis of the Instituto Adolfo Lutz (IAL,
2018). The results of the physicochemical analyzes were submitted to analysis of
variance (ANOVA), and to verify if there was a significant difference in the
data, the Tukey averages tests were applied at the level of 5% of significance
in the variables in the SISVAR program version 5.6 (FERREIRA, 2019).
Resultado e discussão
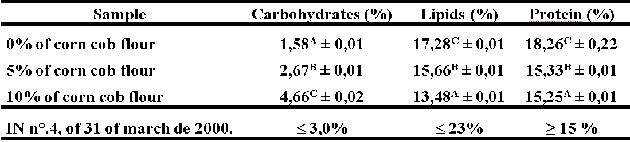
The proximal composition of the hamburger treatments added with 0%, 5% and 10%
corn cob meal is shown in Table 1
The formulations 0% and 5% of corn cob flour showed agreement with the Technical
Regulation on Hamburger Identity and Quality (BRASIL, 2000). The formulation 10%
of corn cob flour presented an average of carbohydrates above the recommended in
the referred legislation. The addition of corn cob flour in the proportions of
5% and 10% significantly interfered with the values of carbohydrates, lipids and
protein. These results may be related to the low levels of protein and moisture
in the corn cob meal and the reduction in the percentage of meat for the
addition of corn cob meal in the formulation. Ferreira (2014) analyzing
hamburgers with the addition of corn cob flour obtained values for protein with
no difference between treatments. Santos Junior; Rizzatti and Brungera (2009),
analyzing hamburgers, also found protein levels between 18.94% and 20.94%, with
no difference between treatments. Traditional hamburgers had lipid content
between 14.28% and 20% (MARQUES, 2007; TAVARES et al, 2017). Madruga et al
(2007) obtained 14.28 and 19.64% of lipids for hamburgers made with sheep and
goat meat, respectively. Marques (2007) performing analysis on samples of bovine
hamburgers made with different percentages of oat flour found a great variation
in the levels of carbohydrates, with the percentage of 2.82% of carbohydrate
found in the formulation with 0% of oat flour and the percentage of 15.02% for
the formulation containing 25% oat flour. Fernandes and Pizato (2019) added
sorghum flour to beef burgers obtained better yield for cooking characteristics,
showing higher yield and lower shrinkage.
Conclusões
The addition of flour significantly altered the physicochemical analyses. The
results of the physicochemical analyzes of the hamburgers made with no addition
and with 5% and 10% of corn cob flour indicated an increase in the carbohydrate
content and a reduction in the lipid and protein content as a result of the
increase in corn cob flour. Complementary studies are necessary for its use and
further research is necessary to define the best way of application in meat
products.
Agradecimentos
To God, to the IFTO Paraiso do Tocantins campus
Referências
FERNANDES, A.B.C., PIZATO, S. Elaboração de hambúrguer de carne bovina com adição de farinha de sorgo (Sorghum Vulgare), Revista PubSaúde. 2, a009. 2019. DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.31533/pubsaude2.a 009
BRASIL. Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento. Aprova os Regulamentos Técnicos de Identidade e Qualidade de Almôndega, de Apresentado, de Fiambre, de Hamburguer, de Kibe, de Presunto Cozido e de Presunto. Instrução Normativa n° 20, de 31 de Julho de 2000. Brasília: Diário Oficial da União de 03 de Agosto de 2000, Seção I, p. 7-12.
BRASIL. Instrução Normativa n°.4, de 31 de março de 2000. Aprova os regulamentos técnicos de identidade e qualidade de carne mecanicamente separada, de mortadela, de linguiça e de salsicha. Diário Oficial da União, Brasília, 05 abr. 2000. Seção 1. p.6.
FASOLIN, L. H. et al. Biscoitos produzidos com farinha de banana: avaliações química, física e sensorial. Revista Ciência e Tecnologia de Alimentos. Campinas, v. 27, n. 3, 2007.
FERREIRA, J. F. Elaboração de hambúrguer bovino adicionado de farelo do urucum (Bixa orellana L.) . 2014. 94 f. Trabalho de conclusão de curso (Graduação)-Universidade Federal da Paraíba, Jõao Pessoa, PB. 2019. Disponivel em: https://repositorio.ufpb.br/jspui/bitstream/123456789/15878/1/JFF25092019.pdf. Acesso em: 22 maio 2022
FERREIRA, S. F. Caracterização de produtos cárneos desenvolvidos com adição de farinha do sabugo de milho (Zea mays). Dissertação. 2014. 94 f. Dissertação (Mestrado)-Universidade Federal de Santa Maria, Santa Maria, RS. 2014. https://repositorio.ufsm.br/bitstream/handle/1/5771/FERREIRA%2c%20SABRINA%20FAGUNDES.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y.
HAUTRIVE, T. P.; OLIVEIRA, V. R.; SILVA, A. R. D.; TERRA, N. N.; CAMPAGNOL, P. C. B. Análise físico-química e sensorial de hambúrguer elaborado com carne de avestruz. Ciência e Tecnologia de Alimentos, Campinas, v. 28, n. 2, p. 95-101, 2008. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0101-20612008000500016.
IAL, Instituto Adolfo Lutz. Métodos físico-químicos para análise de alimentos. São Paulo-SP: IAL. 2018
MADRUGA, M. S. et al.; Carnes caprina e ovina: processamento e fabricação de produtos derivados. Tecnol. & Ciên. Agropecuária. v.1. n.2, p.61-67, 2007.
MARQUES, J. M. Elaboração de um produto de carne bovina “tipo hambúrguer” adicionado de farinha de aveia. 2007. 71f. Dissertação (Mestrado em Tecnologia de Alimentos) – Universidade Federal do Paraná, 2007.
ORTIGOZA, S. A. G. Alimentação e saúde: as novas relações espaço-tempo e suas implicações nos hábitos de consumo de alimentos. RAEGA - O Espaço Geográfico em Análise, Curitiba, n. 15, p. 83-93, 2008. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5380/raega.v15i0.14247. Acesso em: 25 fev. 2022.
ROCHA, Y.J.P. Aplicação de fibra de ervilha em produtos cárneos. 2015. 104 f. Dissertação (Mestrado em Ciências) – Faculdade de Zootecnia e Engenharia de Alimentos, Universidade de São Paulo. Pirassununga. 2015.
SANTOS JUNIOR, L. C. O.; RIZZATTI, R.; BRUNGERA, A. et al. Desenvolvimento de hambúrguer de carne de ovinos de descarte enriquecido com farinha de aveia. Cienc. Anim. Bras. v.10, p.1128-1134, 2009.
TAVARES, R. S. et al. Processamento e aceitação sensorial do hambúrguer de coelho (Orytolagus cunicullus). Ciênc. Tecnol. Alimentos. v.27, n.3, p. 633-636, 2007.
TERRA, N. N. Apontamentos de tecnologia de carnes. São Leopoldo: Unisinos, 2005.
















