Autores
Vargas, D.F. (IQUIR) ; Fonzo, S. (IQUIR) ; Larghi, E.L. (IQUIR) ; Kaufman, T.S. (IQUIR)
Resumo
The synthesis of the typical tricyclic core of cassiarin alkaloids through the use
of C–H activation strategies is described. The use of an O-pivaloyl oxime
(2) allowed to access the tricyclic system of 8-O-methylcassiarin
(3) in 4 and 6 steps with overall yields of 19% and 26% respectively. This
key intermediate could facilitate the synthesis of other natural cassiarins with
additional transformations.
Palavras chaves
Natural Products; C-H activation-Cassiarins; Heterocycles - Synthesis
Introdução
Cassia siamea Lamk (Caesalpiniaceae) is a tropical legume native to
Southeast Asia, which is well known for its nutritional properties and economic
importance. In addition to being used as food, its extract is commonly employed
in traditional Oriental and African medicine to treat periodic fevers and
malaria (KUMAR et al., 2017). The cassiarins, a family of tricyclic alkaloids
which contain an isoquinoline nucleus (AC) fused to a 2-methyl-2H
pyran ring (B), have been isolated from this plant (MORITA et al., 2007;
OSHIMI et al., 2009; LI et al., 2015; WU et al., 2016). On the other hand, the
CAr–H activation reactions have become a modern and increasingly
valuable and attractive approach for the generation of new CAr–R
bonds, averting the multiple functionalization steps required by traditional
chemistry (GANDEEPAN et al., 2019). Therefore, based on our previous experience,
we describe an accessible, short and efficient synthesis of 8-O-
methylcassiarin C (3) using C–H activation strategies.
Material e métodos
All the reactions were carried out under inert atmospheres of anhydrous argon,
employing oven-dried glassware and freshly distilled anhydrous solvents. The
reactions were monitored by TLC, run on Kieselgel 60 GF254 plates, using
hexane:EtOAc solvent mixtures of different polarities. The chromatographic spots
were detected by irradiation of the plates with short wavelength UV light (254
nm), followed by spraying with ethanolic p-anisaldehyde/sulfuric acid. The flash
column chromatographies were developed with slurry-packed silica gel 60 H
(particle size 63–200 μm). The elution was performed under positive pressure,
using gradient of solvent (hexane-EtOAc mixtures) polarity techniques. Melting
points (uncorrected) were measured with an Ernst Leitz Wetzlar model 350 heated
microscope. NMR spectra were obtained in CDCl3 on a Bruker Avance 300
spectrometer (300.13 MHz for 1H, 75.48 MHz for 13C). NOE
and 2D NMR spectra (HSQC, HMBC) were used to complete the elucidation.
Resultado e discussão
The synthetic route (Scheme 1) started with a combined Friedel-Crafts acylation
of 3-methoxyphenol (1) with crotonic acid, followed by a oxa-Michael
addition, which provided chromanone 2. Subsequently, the oximes 2a
were prepared and C–H activation reactions catalyzed by [RuCl2
(p-cymene)]2 and (Cp*RhCl2)2 complexes
were carried out on these in order to synthesize compound 3. A first
approach consisted in the preparation of compound 4 by the C–H
activation-directed allylation of a methoxime (R1 = Me), followed by
a one-pot isomerization/6π-azaelectrocyclization sequence to obtain 3.
This proved to be an unsuccessful strategy. On the other hand, the C–H
activation/cyclization of the O-pivaloyl oxime (R1 = Piv) with
isopropenyl acetate under rhodium(III) catalysis, successfully provided access
to 8-O-methylcassiarin C (3) in a single operation (30% yield).
Thus, the synthesis of this tricyclic isoquinoline was achieved in 4 steps and
19% overall yield. In addition, in a third approach the use of a more electron-
poor olefin (methyl acrylate) allowed the cassiarin ester 5 to be
obtained in 76% yield. Subsequently, the isoquinoline 5 was transformed
into 3 through an ester reduction/deoxygenation sequence. Gratefully,
this 6-stage route increased the overall yield to 26%. The reach of our
synthetic route could be extrapolated to the utilization of 8-O-
methylcassiarin (3) as a common intermediate in the divergent total
synthesis of cassiarin alkaloids. It is expected that it would only take the
effort of a few steps to achieve the alkaloids shown in Scheme 2.
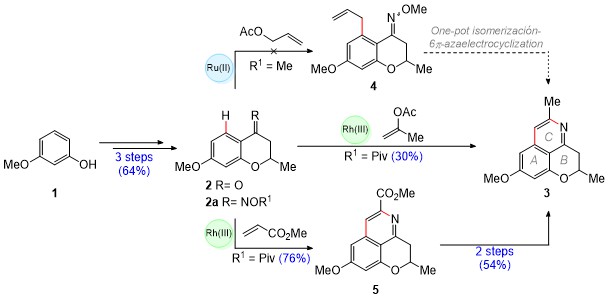
Scheme 1. Synthetic strategies directed towards 8-O- methylcassiarin C (3).

Scheme 2. Outlook of the divergent total synthesis of cassiarin alkaloids.
Conclusões
In this approach, we have achieved access to a key intermediate for the total
synthesis of cassiarin alkaloids through an olefination/annulation process.
According to the three proposed routes, 8-O-methylcassiarin was accessed in
two concise synthetic sequences, in 19 and 26% overall yield.
Agradecimentos
Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (PUE IQUIR 2016 and PIP
0765) and Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (PICT 2018-01933,
and 2017-0149). DFV thanks CONICET (Postdoctoral Fellowship).
Referências
GANDEEPAN, P.; MÜLLER, T.; ZELL, D.; CERA, G.; WARRATZ, S.; ACKERMANN, L. 3d transition metals for C–H activation. Chem. Rev. 2018, 119, 2192-2452.
KUMAR, D.; JAIN, A.; VERMA, A. Phytochemical and pharmacological investigation of Cassia siamea Lamk: An insight. Nat. Prod. J. 2017, 7, 255-266.
LI, L.; LIU, G.; LOU, J.; WANG, H.; YANG, J.; HU, Q.; YE, Y. A new alkaloid from the stem of Cassia siamea and its anti-tobacco mosaic virus activity. Asian J. Chem. 2015, 27, 2349-2350.
MORITA, H.; OSHIMI, S.; HIRASAWA, Y.; KOYAMA, K.; HONDA, T.; EKASARI, W.; INDRAYANTO, G.; ZAINI, N. C. Cassiarins A and B, novel antiplasmodial alkaloids from Cassia siamea. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 3691-3693.
OSHIMI, S.; DEGUCHI, J.; HIRASAWA, Y.; EKASARI, W.; WIDYAWARUYANTI, A.; WAHYUNI, T. S.; ZAINI, N. C.; SHIROTA, O.;MORITA, H. Cassiarins C− E, antiplasmodial alkaloids from the flowers of Cassia siamea. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1899-1901.
WU, H. Y.; HU, W. Y.; LIU, Q.; YU, Z. H.; ZHAN, J. B.; YAN, K. L.; WANG, Y. DE; ZHOU, K.; DONG, W.; LI, Y. K.; ZHOU, M.; HU, Q. F. Three new alkaloids from the twigs of Cassia siamea and their bioactivities. Phytochem. Lett. 2016, 15, 121-124.
















