Realizado no Rio de Janeiro/RJ, de 14 a 18 de Outubro de 2013.
ISBN: 978-85-85905-06-4
ÁREA: Química Analítica
TÍTULO: Thermal behaviour of nicotinic acid, sodium nicotinate and its compounds with some bivalent trasition metal ions.
AUTORES: Nascimento, A. (UNESP ARARAQUARA) ; Caires, F. (UNESP ARARAQUARA) ; Gomes, D. (UNESP ARARAQUARA) ; Gigante, A. (UNESP ARARAQUARA) ; Ionashiro, M. (UNESP ARARAQURA)
RESUMO: Solid-state M(L)2.nH2O compounds, where M stands for bivalent transition metals
(Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu and Zn), L is nicotinate and n= 0 – 4.5, have been
synthesized. Characterization and thermal behaviour of these compounds were
investigated employing some analytical techniques. The results provided
information concerning the thermal stability, thermal decomposition and
identification of the gaseous products evolved during the thermal decomposition of
the compounds.
PALAVRAS CHAVES: bivalent transition metal; nicotinate; thermal behaviour
INTRODUÇÃO: Pyridine-3-carboxylic acid (C6H5NO2), also called 3-picoline or nicotinic acid
is an organic acid whose melting point is 236.6 ºC. It is the biological
precursor of the co-enzymes nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP). A survey of the literature
shows that papers involving bivalent transition metals and nicotinic acid
reported the spectroscopic, thermogravimetric and magnetic studies on some metal
complexes with pyridine carboxylic acid [1], thermochemical behavior of solid
nicotinic hydrazide metal complexes in correlation with their stoichiometry [2],
the thermal decomposition of copper (II)nicotinate and isonicotinate [3], the
polymeric structure of aquacadmiun bis nicotinate [4], a new 2-d
chiralcoordination polymer of [Zn(nicotinate)2]n [5], synthesis and
characterization of copper(II) complexes with nicotinate in different
coordination style [6], simultaneous thermalanalysis of a cobalt(II) complex
with nicotinate [7], hydrothermal synthesis, crystal structures of two 3-D
network nickel nicotinate coordination polymers [8].
In this paper, the object of the present research was to investigate the thermal
behaviour of nicotinic acid and its sodium salt, as well as to prepare solid-
state compound of some bivalent transition metal ions ( i.e Mn(II), Fe(II),
Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II) ) with nicotinate and to characterize and to
investigate by means of complexometry, elemental analysis, X-ray diffractometry,
infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), simultaneous thermogravimetry and differential
thermal analysis (TG-DTA), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and TG-DSC
coupled to FTIR. The thermal studies were performed in dynamic air atmosphere.
MATERIAL E MÉTODOS: The nicotinic acid (C6H5NO2) with 99.5% purity was obtained from Sigma and it
was used as received. Aqueous solution of sodium nicotinate 0.1 mol L-1 was
prepared by neutralization of an aqueous solution of nicotinic acid with sodium
hydroxide solution 0.1 mol L-1. Aqueous solutions of bivalent metal ions 0.1 mol
L-1 were prepared by dissolving the corresponding chloride ( Mn(II), Co(II),
Ni(II) ) or sulphate ( Fe(II), Cu(II), Zn(II) ).
The solid-state compounds were obtained by adding slowly with stirring 100 mL of
sodium nicotinate solution 0.1 mol L-1 to 50 mL of the respective metal ions
solutions 0.1 mol L-1 heated up to near ebullition. The system was cooled up to
ambient temperature and the precipitates were filtered off, washed with
distilled water until chloride or sulphate ions were eliminated (qualitative
test with AgNO3/HNO3 solution for chloride ions or BaCl2 solution for sulphate),
dried at 50 ºC in a forced circulation air oven during 12h and kept in a
desiccator over anhydrous calcium chloride. To avoid the oxidation of Fe(II),
all the solutions, as well the water employed for washing the precipitate were
purged with nitrogen gas, even during the heating up to near ebullition and
cooling up to ambient temperature.
Simultaneous TG-DTA curves were obtained with thermal analysis system, model SDT
2960 from TA Instruments. The purge gas was an air flow of 100 mL min-1. A
heating rate of 10 ºC min-1 was adopted, with samples weighing about 7 mg.
Alumina crucibles were used for recording the curves.
RESULTADOS E DISCUSSÃO: Simultaneous TG-DTA curves of the compounds are show in Fig. 1. These curves
show mass losses in a single, two or three steps and thermal events
corresponding to these losses or due to physical phenomenon.
These curves also show that the thermal stability of the hydrated compounds (I),
of the anhydrous ones (II), as well as the final temperature of thermal
decomposition depend on the nature of the metal ion, and they follow the order:
(I) Mn > Ni > Co > Fe > Cu
(II) Mn > Co > Zn > Ni > Cu > Fe
(III) Zn > Mn > Co > Cu > Ni > Fe
The thermal behavior of the compound is also dependent on the nature of the
metal ion and so the features of each of these compounds are discussed
individually in full work.
For the manganese, iron, cobalt and nickel compounds, the difference observed in
the peak temperature of dehydration in the DTA curves is undoubtedly due to the
experimental conditions which were not the same. The dehydration and crystalline
phase transition enthalpies found for the compounds were, respectively: 148.5
(Mn), 223.6 (Fe), 260.8 (Co) and 256.9 (Ni) kJ mol-1.
The gaseous products evolved during the thermal decomposition of the sodium and
the transition metal ion compounds studied in this work were monitored by FTIR,
and they have carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, pyridine and indicium of N2O. The
IR spectra of the gaseous products evolved during the thermal decomposition of
these compounds are show in Fig. 2.
The results establish the stoichiometry of these compounds, which are in
agreement with the general formula: M(L)2.nH2O, where M represents Mn(II),
Fe(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II), L is nicotinate and n= 0 (Zn); 0.25
(Cu); 2 (Mn); 3.5 (Fe) and 4.5 (Co, Ni).
Figure 1
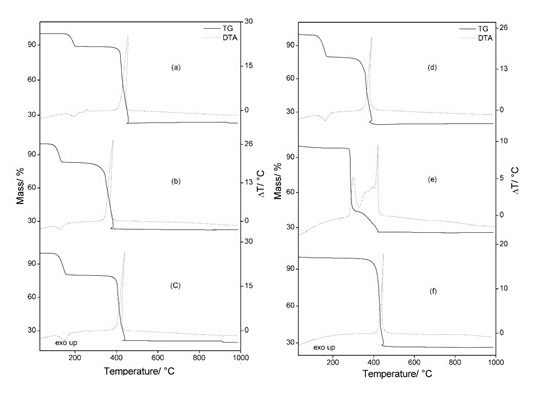
Simultaneous TG-DTA curves of the compounds: (a)
Mn(7.045mg), (b) Fe(7.080mg), (c) Co(7.099mg), (d)
Ni(7.081mg), (e) Cu(7.006mg) and (f) Zn(7.038mg).
FIgure 2
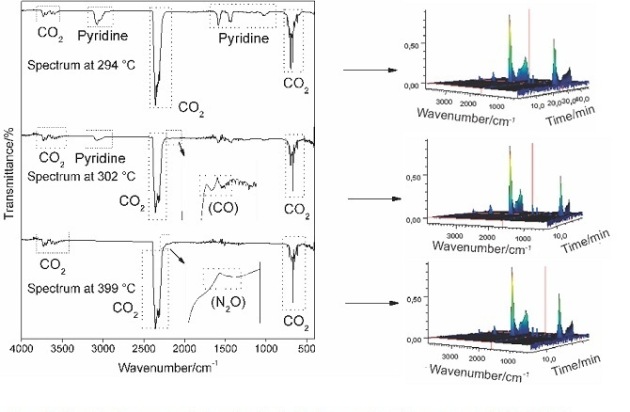
IR spectra of gaseous products evolved during the
decomposition of the compounds: Cu(L)2.0,25H2O.
CONCLUSÕES: From TG, complexometry and elemental analysis results, a general formula
could be established for the synthesized compounds.
The simultaneous TG-DTA and DSC curves provided previously unreported
information about the thermal stability and thermal decomposition of these
compounds in dynamic air atmosphere, and the thermal study of iron compound have
been reported for the first time.
The monitoring of the evolved gases during the thermal decomposition of
the metal nicotinates occurs with release of CO, CO2 and pyridine.
AGRADECIMENTOS: The authors thank FAPESP, CNPq and CAPES foundations (Brazil) for financial
support.
REFERÊNCIAS BIBLIOGRÁFICA: [1] A. Kleinstein, G.A. Webb, Spectroscopic, thermogravimetric and magnetic studies on some metal complexes with pyridine carboxylic acids, J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem 33(1971) 405-412.
[2] M.M.A. Sekkina, M.G.A. El-Azm, Thermochemical behaviour of solid nicotinic hydrazide metal complexes in correlation with their stoichiomety, thermochim. Acta 77 (1984) 211-218.
[3] E.E. Sileo, P.J. Morando, C.O.D. Vedova, M.A. Blesa, The thermal decomposition of copper (II) nicotinate and isonicotinate, Thermochim. Acta 138 (1989) 233-239.
[4] W. Clegg, J.T. Gressey, A. Mac Camley, B.P. Straughan, The polymeric structure of aquacadmiumbisnicotinate,ActaCryst. CSI (1995) 234-235.
[5] J.Y. LU, E.E. Kohler, A new 2-D chiral coordination polymer of [Zn(nicotinate)2]n, Inorg. Chem. Commun, 5 (2002) 600-601.
[6] F. Nie, Y. Deng, Y. Li, Y Zhao, Synthesis and characterization of copper (II) complexes with nicotinate in different coordenation style, J. Inorg. Biochem 96 (2003) 201.
[7] Y. Liu, J. Yu, J. Zhao, H. Zhaug, Y. Deng, Z. Wang, Simultaneous thermal analysis of a cobalt (II) complex with nicotinate, Thermochim. Acta 419 (2004) 115-117.
[8] A.E. Wasson, R.L. La Duca, Hydrothermal synthesis crystal structures of two 3-D network nickel nicotinate coordination polymers, Polyhedron 26 (2007) 1001-1011.
